Leveraging Big Data for Improved Patient Outcomes
The healthcare landscape is undergoing a transformation, with Big Data at the forefront of improving patient outcomes. Across the world, and particularly in India, data-driven insights are helping doctors and healthcare institutions make better decisions, optimize resources, and offer personalized care. From predicting disease outbreaks to tailoring treatments based on genetic profiles, Big Data is revolutionizing medicine in ways previously unimaginable.
The Role of Big Data in Healthcare
Big Data in healthcare refers to the massive volumes of structured and unstructured information generated from electronic health records (EHRs), medical imaging, wearable devices, and mobile health applications. The goal is to analyze and utilize this data to enhance clinical decision-making, streamline hospital operations, and improve public health outcomes.
Dr. Atul Butte, a bioinformatics expert at the University of California, emphasizes the potential of Big Data in medicine:
“We have more data than ever before—our challenge is to transform that data into knowledge and action to help patients.”
Transforming Clinical Decision-Making
One of the most significant benefits of Big Data is its impact on diagnostics and treatment planning. Predictive analytics, powered by machine learning, allows physicians to assess a patient’s risk for diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and tuberculosis.
For instance, the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) uses data analytics to predict tuberculosis hotspots, allowing health authorities to intervene early. Similarly, AI-driven platforms like IBM Watson for Oncology analyze vast datasets of cancer patient records to recommend personalized treatment plans.
Case Study: AI-Powered Diagnostics in India
Apollo Hospitals has implemented AI tools to analyze radiology scans, reducing diagnostic errors and improving early detection of conditions like lung cancer. The AI system, trained on millions of medical images, assists radiologists in detecting abnormalities that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Dr. Prathap Reddy, founder of Apollo Hospitals, highlights this shift:
“AI and Big Data are empowering doctors with the right tools to provide faster and more accurate diagnoses, ultimately saving lives.”
Big Data and Personalized Medicine
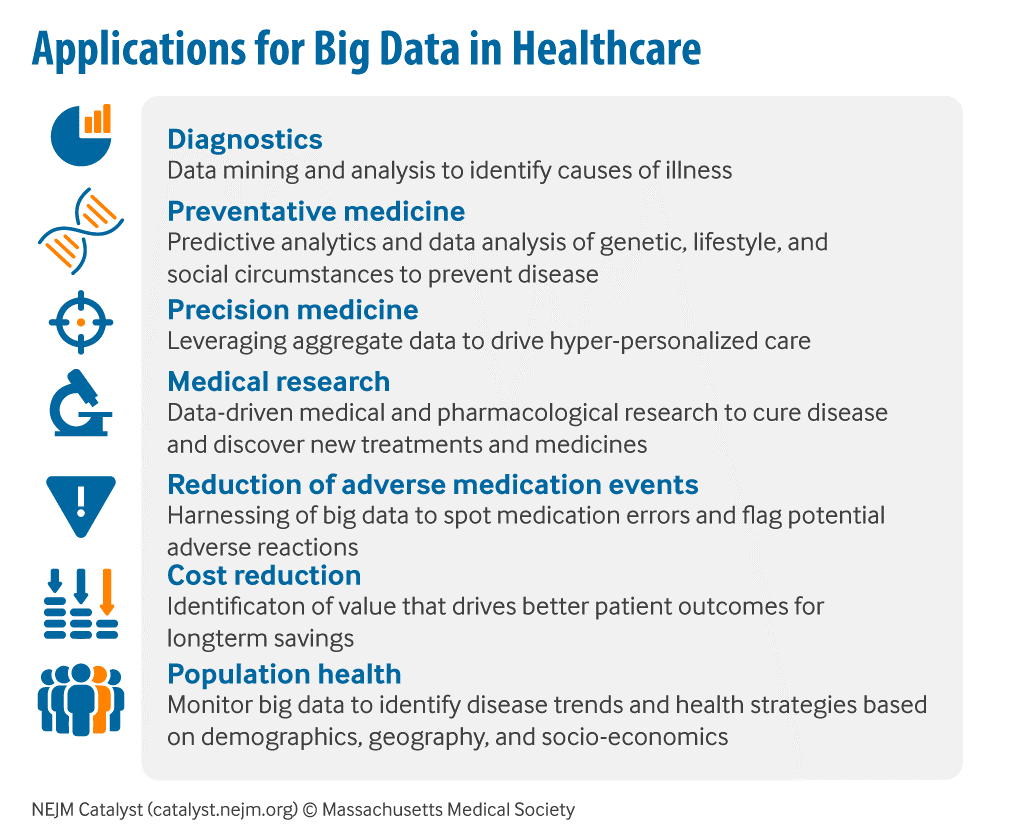
Personalized medicine tailors’ treatment based on an individual’s genetic profile, lifestyle, and environment. This approach is particularly relevant in India, given the country’s genetic diversity.
Tata Memorial Hospital in Mumbai has adopted genomic sequencing to customize cancer treatments. By analyzing genetic mutations, doctors can identify the most effective therapies, minimizing trial-and-error approaches.
Pharmaceutical companies are also leveraging Big Data to develop precision medicines. Companies like Roche and Novartis use patient data from clinical trials to design targeted drugs with fewer side effects.
India faces a growing burden of chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular conditions. Big Data enables continuous monitoring and timely interventions.
Startups like HealthifyMe and GOQii are using wearable technology and AI to track patient health in real time. A diabetic patient using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) can have their data analyzed instantly, allowing their doctor to adjust medication and lifestyle recommendations proactively.
Dr. Devi Shetty, founder of Narayana Health, stresses the importance of such innovations:
“Remote monitoring and data-driven interventions are the future of chronic disease management, especially in a country as vast as India.”
Public Health and Disease Prevention
Big Data is crucial in tracking and preventing outbreaks of infectious diseases. By analyzing data from hospitals, pharmacies, and even social media, health authorities can predict and contain epidemics.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, India’s Aarogya Setu app leveraged real-time data to identify infection clusters, enabling targeted lockdowns and medical interventions. The Indian government also used data from testing centers and hospitals to allocate resources efficiently.
Additionally, researchers at the Public Health Foundation of India (PHFI) use predictive modeling to monitor vector-borne diseases like dengue and malaria, allowing for timely public health responses.
Optimizing Hospital Operations

Big Data doesn’t just improve patient care—it also enhances hospital efficiency. Predictive analytics helps hospitals manage patient loads, optimize staffing, and reduce wait times. Medanta – The Medicity Hospital in Gurugram employs AI-powered predictive analytics to estimate emergency room admissions based on historical trends. This allows hospital administrators to allocate resources effectively, reducing congestion and improving patient care.
Overcoming Challenges: Privacy, Infrastructure, and Data Quality
Despite its advantages, implementing Big Data in Indian healthcare comes with challenges:
- Data Privacy: Patient confidentiality is a major concern. The Digital Information Security in Healthcare Act (DISHA) is being developed to regulate data security in India.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Many rural areas lack the digital infrastructure needed for real-time data collection and analysis.
- Data Quality: Inconsistent data collection practices can lead to errors in analysis and decision-making.
Addressing these challenges will require government investment, stringent data regulations, and better training for healthcare professionals.
The Future of Big Data in Indian Healthcare
India is at a pivotal moment in its healthcare transformation. With initiatives like the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM), which aims to create a unified digital health ecosystem, Big Data will play an even bigger role in shaping the future of medicine.
The Future of Big Data in Indian Healthcare
India is on the brink of a digital healthcare revolution, with Big Data at its core. As technology advances and healthcare systems become more interconnected, Big Data is set to play a pivotal role in transforming patient care, optimizing resources, and improving public health strategies. The Indian government, private healthcare providers, and technology companies are all investing in data-driven solutions to bridge gaps in accessibility, affordability, and quality of care.
One of the most promising aspects of Big Data in Indian healthcare is its integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies enable the analysis of massive datasets to uncover patterns, predict health risks, and personalize treatments. AI-driven algorithms can process vast amounts of patient data—including medical histories, imaging scans, and genetic information—to assist doctors in making faster and more accurate diagnoses.

For example, AI-based diagnostic tools are already being used to detect diseases such as tuberculosis and diabetic retinopathy in India. Google’s DeepMind has developed AI models capable of analyzing retinal scans with high precision, potentially preventing blindness in diabetic patients. Similarly, AI-powered pathology tools are enhancing cancer detection, allowing for early intervention and improved survival rates.
As AI models continue to evolve, their predictive capabilities will help doctors anticipate disease outbreaks, track patient deterioration in real-time, and develop proactive healthcare strategies. This will significantly reduce hospitalization rates, improve preventive care, and enhance overall patient outcomes.
Expansion of the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM)
The National Digital Health Mission (NDHM) is a key government initiative aimed at creating a unified digital healthcare ecosystem in India. NDHM seeks to digitize health records, making patient data easily accessible to authorized healthcare providers. This initiative will improve coordination among hospitals, reduce duplication of tests, and enable seamless patient care.
With NDHM’s implementation, patients will have unique health IDs, allowing them to securely store and share their medical history with different healthcare providers. This will be especially beneficial for individuals with chronic conditions who require long-term monitoring and management. By leveraging Big Data, NDHM can also help policymakers identify healthcare trends and allocate resources efficiently, ensuring better healthcare delivery across urban and rural areas.
Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring
With India’s vast geography and uneven distribution of healthcare facilities, telemedicine and remote patient monitoring powered by Big Data will play a crucial role in improving accessibility. Telemedicine platforms like Practo, 1mg, and Tata Health are already connecting patients with doctors virtually, reducing the need for in-person visits.
Big Data enhances telemedicine by allowing doctors to analyze patient data remotely, track disease progression, and offer real-time recommendations. For instance, wearable devices like continuous glucose monitors and smartwatches collect patient data on heart rate, blood sugar levels, and physical activity. This data is transmitted to healthcare providers, enabling proactive interventions and reducing complications from chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension.
As 5G networks expand, telemedicine services will become more efficient, providing high-quality virtual consultations even in remote areas. This will be particularly beneficial for elderly patients, those with mobility issues, and individuals living in rural regions with limited healthcare access.
Big Data for Public Health and Policy Making
Big Data is not just transforming individual patient care but also shaping public health policies and epidemic management. By analyzing data from hospitals, pharmacies, and digital health platforms, governments can identify disease trends and allocate resources effectively.

During the COVID-19 pandemic, India used Big Data to track infections, optimize vaccine distribution, and implement targeted lockdowns. Future pandemics and outbreaks of diseases like dengue and malaria can be managed more effectively using predictive modeling and real-time surveillance.
Additionally, Big Data can help policymakers design targeted healthcare programs for maternal and child health, malnutrition, and non-communicable diseases. For example, by analyzing demographic and lifestyle data, health officials can launch awareness campaigns to promote vaccinations, early screenings, and preventive healthcare measures.
Challenges and the Way Forward
While the potential of Big Data in Indian healthcare is immense, several challenges must be addressed:
- Data Privacy and Security: Patient data security is a major concern. Implementing strict data protection regulations under frameworks like the Digital Information Security in Healthcare Act (DISHA) will be critical in ensuring patient confidentiality.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity: Many rural areas lack the digital infrastructure required for real-time data collection and telemedicine services. Expanding internet connectivity and digital health infrastructure will be essential.
- Data Standardization: With multiple hospitals and healthcare providers using different systems, creating a standardized and interoperable data-sharing framework will improve efficiency and reduce errors.
The future of Big Data in Indian healthcare is promising, with advancements in AI, personalized medicine, telehealth, and public health analytics shaping a more efficient and patient-centric system. As government initiatives like NDHM gain momentum and private players continue to innovate, data-driven healthcare will become more accessible, proactive, and precise.
By addressing existing challenges and embracing digital transformation, India can build a robust healthcare ecosystem that not only improves individual patient care but also strengthens public health strategies for a healthier future.
As Dr. Eric Topol, a renowned cardiologist and digital health expert, puts it:
“The convergence of Big Data and AI is not just the future of medicine—it is the present. We must embrace it to make healthcare more efficient, effective, and equitable.”
By integrating Big Data analytics, AI, and digital health initiatives, India can bridge healthcare gaps, improve patient outcomes, and revolutionize the way medicine is practiced.
Conclusion
Big Data is no longer a futuristic concept—it is already transforming Indian healthcare. From AI-powered diagnostics and personalized treatments to chronic disease management and hospital optimization, data-driven insights are enhancing patient care. While challenges remain, the potential for Big Data to revolutionize healthcare is undeniable.
By embracing this digital transformation, India can build a more efficient, data-driven healthcare system that improves lives at scale.
References:
- http://1. Big data in healthcare: management, analysis and future prospects | Journal of Big Data | Full Text
- http://2. Leveraging big data analytics in healthcare enhancement: trends, challenges and opportunities | Multimedia Systems
- http://3. Big Data Capabilities for Hospital: A Systematic Literature Review – ScienceDirect
- http://4. Challenges and Opportunities of Big Data in Health Care: A Systematic Review – PMC
- http://5. (PDF) Leveraging Big Data Analytics to Improve Quality of Care in Healthcare Organisations: A Configurational Perspective